Dorsalgia is a medical term that refers to pain in the upper back or thoracic spine area. This condition can range from a dull ache to sharp, severe pain that limits a person’s ability to perform daily activities. Veterans often experience dorsalgia due to the physical demands of military service, which can put significant stress on the back muscles and spine.
Common causes of dorsalgia include muscle strain, poor posture, repetitive motions, and injuries sustained during military training or combat. For many veterans, carrying heavy gear, long marches, and operating equipment for extended periods can contribute to the development of chronic back pain.
Additionally, traumatic events such as explosions or vehicle accidents during deployment can lead to long-lasting dorsalgia.
It’s important to note that dorsalgia can also be a symptom of other underlying conditions, such as degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, or osteoarthritis. These conditions may develop over time or be exacerbated by the physical demands of military service.
How the VA Defines Dorsalgia

The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) recognizes dorsalgia as a compensable condition for disability benefits. However, the VA does not have a specific rating for “dorsalgia” itself. Instead, it evaluates back pain and related conditions under the broader category of musculoskeletal disorders, specifically focusing on the spine.
When assessing dorsalgia claims, the VA considers the impact of the condition on a veteran’s daily life and ability to work. The evaluation typically involves looking at factors such as range of motion, pain levels, and functional limitations. The VA may also consider any neurological symptoms associated with the back pain, as these can significantly affect a veteran’s overall disability rating.
It’s crucial for veterans to understand that the VA’s definition of dorsalgia is not limited to a single diagnosis. Rather, it encompasses a range of back-related issues that can cause pain and limitation in the upper back area. This broad approach allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of a veteran’s condition.
Eligibility Criteria for Dorsalgia VA Rating
To be eligible for a VA disability rating for dorsalgia, veterans must meet certain criteria. First and foremost, there must be a clear connection between the current back condition and the veteran’s military service. This connection is known as a “service connection” and is crucial for establishing eligibility for VA benefits.
Veterans need to provide evidence that their dorsalgia either began during active military service, was aggravated by service, or is directly related to an event or injury that occurred during service. This evidence can include medical records from during service, statements from fellow service members, and current medical diagnoses that link the condition to military service.
Additionally, veterans must demonstrate that their dorsalgia results in a current disability that impacts their daily life and ability to work. The VA will consider the severity of symptoms, frequency of flare-ups, and any limitations on activities when determining the appropriate disability rating.
It’s important to note that even if a veteran’s dorsalgia developed after leaving the military, they may still be eligible for benefits if they can prove that it is secondary to another service-connected condition. For example, if a veteran has a service-connected knee injury that causes them to alter their gait, leading to back pain, they may be able to claim dorsalgia as a secondary condition.
Understanding VA Disability Ratings for Back Pain
The VA uses a standardized system to assign disability ratings for back conditions, including dorsalgia. These ratings are based on the severity of the condition and its impact on the veteran’s life. The ratings range from 0% to 100%, with higher percentages indicating more severe disabilities and resulting in greater compensation.
For back pain, including dorsalgia, the VA primarily considers the range of motion of the spine and the presence of other symptoms such as muscle spasms or abnormal spinal curvature. The rating system is designed to reflect the degree of functional loss and pain experienced by the veteran.
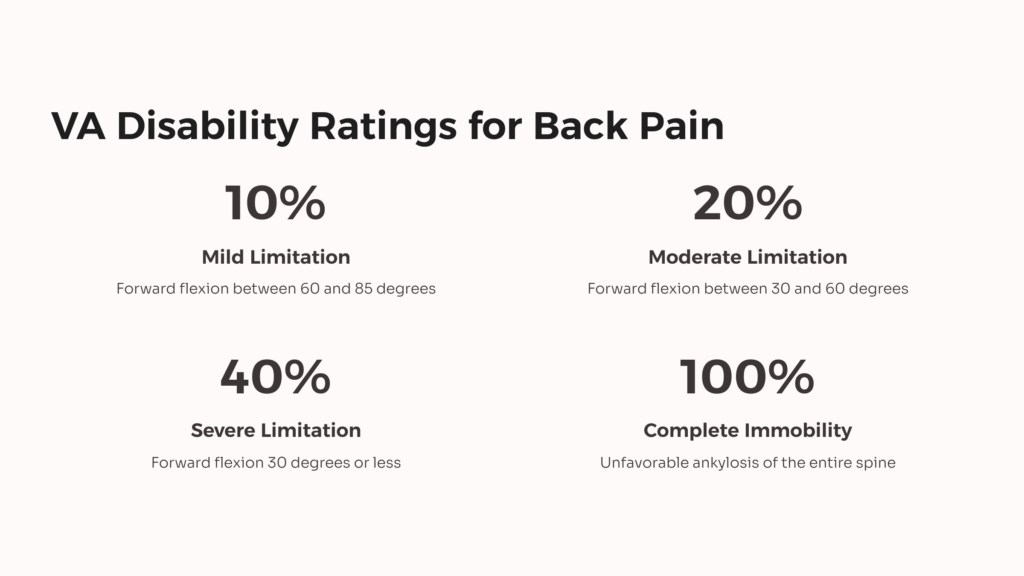
According to CCK Law, VA generally rates low back pain as follows:
- 10% – Forward flexion of the thoracolumbar spine between 60 and 85 degrees
- 20% – Forward flexion between 30 and 60 degrees
- 40% – Forward flexion 30 degrees or less
- 50% – Unfavorable ankylosis of the entire thoracolumbar spine
- 100% – Unfavorable ankylosis of the entire spine
It’s important to understand that these ratings are not just based on pain alone, but on how the pain and associated symptoms limit the veteran’s ability to move and function. Veterans should be prepared to describe in detail how their dorsalgia affects their daily activities and work capabilities when applying for benefits.
General Rating Formula for Diseases and Injuries of the Spine
The VA uses the General Rating Formula for Diseases and Injuries of the Spine to evaluate most back conditions, including dorsalgia. This formula provides a standardized approach to rating spinal disorders based on objective criteria, primarily focusing on range of motion and other measurable factors.
Under this formula, the VA considers several key elements:
1. Range of motion measurements for forward flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation
2. The presence of muscle spasm, guarding, or localized tenderness
3. Abnormal gait or spinal contour
4. The occurrence of incapacitating episodes (for intervertebral disc syndrome)
The ratings are assigned based on the severity of these symptoms and their impact on the veteran’s functionality. For example, a veteran with dorsalgia who experiences muscle spasms severe enough to result in an abnormal gait might receive a 20% rating, even if their range of motion is not significantly limited.
It’s crucial for veterans to understand that this formula applies to the thoracolumbar spine (the middle and lower back) as a whole. The VA does not typically assign separate ratings for different sections of the back unless there are distinct and separate conditions affecting different areas.
How Range of Motion Impacts VA Ratings
Range of motion is a critical factor in determining VA disability ratings for dorsalgia and other back conditions. The VA uses specific measurements to assess how limited a veteran’s back movement is, which directly correlates to the assigned disability percentage.
For dorsalgia affecting the thoracolumbar spine, the VA considers the following range of motion measurements:
- Forward flexion: Bending forward at the waist* Extension: Bending backward
- Lateral flexion: Bending sideways to the left and right
- Rotation: Twisting to the left and right
The most significant of these is forward flexion, as it often has the greatest impact on daily activities. Normal forward flexion of the thoracolumbar spine is considered to be 90 degrees. As the range of motion decreases, the disability rating increases.
It’s important for veterans to understand that pain during movement can affect the range of motion measurements. According to the VA Claims Insider, veterans should be open and honest during their Compensation and Pension (C&P) exam and should stop the examiner as soon as they feel any pain during range of motion tests.
Additionally, the VA must consider factors such as pain, weakness, fatigability, and incoordination when assessing range of motion. This means that even if a veteran can achieve a certain range of motion, if it causes significant pain or if they can’t repeat the motion multiple times due to weakness or fatigue, this should be taken into account in the rating decision.
Common Diagnostic Codes for Dorsalgia
When filing a claim for dorsalgia, veterans may encounter various diagnostic codes used by the VA to classify and rate back conditions. Understanding these codes can help veterans better navigate the claims process and ensure their condition is accurately represented.
Some common diagnostic codes related to dorsalgia include:
- 5237: Lumbosacral or cervical strain
- 5238: Spinal stenosis
- 5239: Spondylolisthesis or segmental instability
- 5242: Degenerative arthritis of the spine
- 5243: Intervertebral disc syndrome
Each of these codes is rated under the General Rating Formula for Diseases and Injuries of the Spine, with the exception of Code 5243 (Intervertebral disc syndrome), which can be rated either under the General Formula or based on the frequency of incapacitating episodes.
It’s important to note that the VA will assign the diagnostic code that best represents the veteran’s condition and results in the highest possible rating. In some cases, multiple codes may be applicable, but the VA generally avoids “pyramiding,” or compensating the same symptom under multiple diagnostic codes.
Veterans should work closely with their healthcare providers and, if possible, a veterans service organization or VA-accredited attorney to ensure their dorsalgia is properly classified and rated under the most appropriate diagnostic code.
How to File a VA Claim for Dorsalgia

Filing a VA claim for dorsalgia requires careful preparation and attention to detail. The process can seem daunting, but breaking it down into steps can make it more manageable. Here’s a guide to help veterans navigate the claim process:
1. Gather evidence: Collect all relevant medical records, including service treatment records, private medical records, and VA medical records. Also gather any supporting statements from fellow service members or family members who can attest to your condition.
2. Complete VA Form 21-526EZ: This is the Application for Disability Compensation and Related Compensation Benefits. You can file this form online through the VA’s eBenefits portal, by mail, or in person at a VA regional office.
3. Provide a personal statement: Write a detailed statement explaining how your dorsalgia is related to your military service and how it affects your daily life and ability to work.
4. Submit your claim: Once you’ve gathered all necessary documents, submit your claim through your chosen method.
5. Attend C&P exam: The VA may schedule you for a Compensation and Pension examination to assess the severity of your condition. Be honest and thorough during this exam.
6. Wait for a decision: The VA will review your claim and send you a decision letter. This process can take several months.
Remember, the key to a successful claim is providing clear, detailed evidence that links your dorsalgia to your military service and demonstrates its impact on your life. Don’t hesitate to seek help from a Veterans Service Organization or a VA-accredited attorney if you need assistance with your claim.
Appealing a Low Dorsalgia VA Rating
If you receive a low rating for your dorsalgia or your claim is denied, you have the right to appeal the VA’s decision. The appeals process can be complex, but understanding your options can help you navigate it more effectively.
Under the new Appeals Modernization Act (AMA), veterans have three options for appealing a VA decision:
1. Higher-Level Review: You can request a senior VA employee to review your case. No new evidence can be submitted with this option.
2. Supplemental Claim: This allows you to submit new and relevant evidence to support your claim.
3. Appeal to the Board of Veterans’ Appeals: You can appeal directly to the Board, choosing from three different dockets (direct review, evidence submission, or hearing).
When appealing a dorsalgia rating, consider the following:
- Review the rating decision carefully to understand why you received a low rating or denial.
- Gather any additional medical evidence that supports a higher rating, such as more recent treatment records or medical opinions.
- Consider obtaining a private medical opinion that addresses the VA’s rating criteria for back conditions.
- Be prepared to explain how your dorsalgia impacts your daily life and ability to work, providing specific examples.
Remember, the appeal process can be lengthy, but persistence can pay off. Many veterans successfully increase their ratings through appeals. Don’t hesitate to seek assistance from a Veterans Service Organization or a VA-accredited attorney, as they can provide valuable guidance throughout the appeals process.
Tips for Maximizing Your Dorsalgia VA Disability Benefits
Maximizing your VA disability benefits for dorsalgia requires a strategic approach and thorough documentation. Here are some tips to help you get the most accurate rating for your condition:
1. Keep detailed records: Document all medical treatments, medications, and how dorsalgia affects your daily life. This includes keeping a pain journal to track the frequency and severity of your symptoms.
2. Attend all medical appointments: Regular medical care not only helps manage your condition but also provides ongoing documentation of your dorsalgia.
3. Be thorough in your C&P exam: During your exam, clearly communicate all symptoms and limitations. Don’t downplay your pain or difficulties.
4. Consider secondary conditions: If your dorsalgia has led to other health issues, such as depression or sleep disorders, you may be eligible for additional ratings for these secondary conditions.
5. Understand the rating criteria: Familiarize yourself with how the VA rates back conditions. This knowledge can help you communicate your symptoms more effectively.
6. Obtain buddy statements: Statements from family, friends, or fellow service members can provide valuable insight into how your condition affects your daily life.
7. Consider unemployability: If your dorsalgia severely impacts your ability to work, you may be eligible for Total Disability based on Individual Unemployability (TDIU).
8. Stay informed about VA updates: VA policies and procedures can change. Stay informed about any updates that might affect your benefits.
Remember, the goal is to ensure that your VA disability rating accurately reflects the full impact of your dorsalgia on your life. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you’re unsure about any part of the process.
Secondary Conditions Related to Dorsalgia
Dorsalgia can often lead to or exacerbate other health conditions, which the VA refers to as secondary conditions. Recognizing and claiming these secondary conditions can significantly impact a veteran’s overall disability rating and compensation.
Common secondary conditions related to dorsalgia include:
1. Radiculopathy: Pain, numbness, or weakness radiating down the arms or legs due to compressed nerves in the spine.
2. Mental health conditions: Chronic pain from dorsalgia can lead to depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders.
3. Gastrointestinal issues: Some veterans develop digestive problems due to long-term use of pain medications for dorsalgia.
4. Hip or knee problems: Altered gait or posture due to back pain can lead to issues in other joints.
5. Headaches: Tension in the upper back and neck can cause chronic headaches.
To claim a secondary condition, veterans need to provide medical evidence linking the new condition to their service-connected dorsalgia. This often requires a medical opinion from a healthcare provider.
It’s important to note that secondary conditions are rated separately from the primary condition. This means that even if a veteran is already receiving the maximum rating for their dorsalgia, they can still receive additional compensation for related secondary conditions.
Veterans should be proactive in discussing any new symptoms or conditions with their healthcare providers and consider whether these might be related to their service-connected dorsalgia. Claiming secondary conditions can lead to a more comprehensive disability rating that better reflects the full impact of the veteran’s service-connected health issues.
Resources for Veterans with Dorsalgia

Veterans dealing with dorsalgia have access to various resources that can provide support, information, and assistance. Here are some valuable resources to consider:
1. VA Health Care: Eligible veterans can receive comprehensive care for their dorsalgia through VA medical centers and clinics. This includes access to pain management specialists, physical therapy, and other treatments.
2. Veteran Service Organizations (VSOs): Organizations like the Disabled American Veterans (DAV), Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW), and American Legion offer free assistance with VA claims and appeals.
3. VA’s Pain Management Resources: The VA offers a Pain Management website with information on pain management strategies and treatments.
4. Vet Centers: These community-based centers provide a range of social and psychological services to veterans and their families, which can be helpful for coping with chronic pain.
5. VA’s MOVE! Weight Management Program: For veterans whose dorsalgia is exacerbated by excess weight, this program offers support for healthy lifestyle changes.
6. My HealtheVet: This online portal allows veterans to access their VA health records, refill prescriptions, and communicate with their healthcare team.
7. Veterans Crisis Line: For veterans experiencing mental health crises related to chronic pain, this confidential support is available 24/7 at 1-800-273-8255 (press 1).
8. VA Adaptive Sports Programs: These programs can help veterans stay active and manage pain through adapted physical activities.
9. VA Caregiver Support: For veterans whose dorsalgia requires assistance from a caregiver, the VA offers support and resources for caregivers.
10. National Resource Directory: This website connects veterans with support services, including those related to health and wellness.
Remember, you’re not alone in dealing with dorsalgia. These resources can provide valuable support and information to help you manage your condition and navigate the VA system. Don’t hesitate to reach out and take advantage of the services available to you as a veteran. Take our free medical evidence screening today at AllVeteran.com and begin your benefits journey today.
 AllVeteran.com Advisors
AllVeteran.com Advisors
With expertise spanning local, state, and federal benefit programs, our team is dedicated to guiding individuals towards the perfect program tailored to their unique circumstances.


















